Top 9 FAQs about Choosing a Wood Engraving Machine
Choosing the right wood engraving machine involves more than comparing prices or power ratings.
Different engraving methods—such as laser engraving and CNC carving—are designed for different materials, depth requirements, and skill levels.
Understanding these differences is essential for selecting a laser engraver for wood that matches your specific projects and long-term goals.
This FAQ guide addresses the top 9 most common questions people ask when choosing a wood engraving machine.
Q1: What Machines Can Engrave Wood
Wood can be engraved using several types of machines, with suitability depending on the required precision, depth, and production scale.
The most commonly used options are laser engravers, CNC routers, and rotary engraving tools.
Laser engravers are widely used for wood engraving when precision, repeatability, and clean detail are required.
CO₂ and diode laser engravers typically produce consistent surface engraving and are commonly used for decorative patterns, text, and surface-level 3D effects.
Laser engravers are generally considered suitable for both home and professional use when proper ventilation and safety measures are in place.

CNC routers are typically used when deeper material removal or structural carving is required.
They are commonly applied in woodworking projects that involve thick materials, complex relief carving, or functional components.
CNC machines are generally preferred in workshop or industrial settings due to their size, cutting forces, and setup requirements.

Rotary engraving tools, such as handheld rotary tools or light-duty desktop engravers, are used for basic or artistic wood engraving.
These tools typically require manual control and are most suitable for small-scale projects or applications where precision and repeatability are less critical.
In summary, laser engravers are commonly used for precise surface engraving, CNC routers are preferred for deep carving and structural work, and rotary tools are generally limited to light or manual engraving tasks.

Q2: How Does a Wood Engraving Machine Work
A wood engraving machine works by removing or altering material from the wood surface in a controlled and repeatable way, based on digital design instructions.
The exact mechanism depends on the machine type, but the operating principle is consistent: a tool or energy source follows programmed paths to create engraved patterns.
Laser engraving machines operate by directing a focused laser beam onto the wood surface.
The laser heats the material to the point of burning or vaporization, removing material without physical contact.
Engraving depth and contrast are typically controlled by laser power, engraving speed, and the number of passes.
Laser engravers are commonly used for detailed surface engraving and shallow 3D relief effects where precision and consistency are required.

CNC engraving machines use a rotating cutting tool that physically removes wood material. The cutting bit follows toolpaths generated from CAD/CAM software, allowing precise control over depth and shape.
CNC machines are generally used when deeper engraving, carving, or structural shaping is required.
Rotary or handheld engraving tools rely on direct mechanical contact and manual guidance.
These tools remove material through abrasion or cutting and are typically limited to light engraving or artistic applications.
In all cases, the engraving process is guided by software that translates a digital design into machine movements, ensuring accurate and repeatable results under defined operating conditions.
Q3: Laser vs CNC for Wood Engraving
Laser engraving and CNC engraving are both established methods for engraving wood, but they are designed for different technical objectives and are typically chosen based on depth requirements, precision, and production context.
- Laser engraving uses a focused laser beam to burn or vaporize the wood surface.
It is generally used for high-detail surface engraving, including text, logos, images, and shallow 3D relief effects.
Laser engraving is typically faster for surface work, requires minimal material setup, and offers high repeatability.
However, engraving depth is limited, and it is not intended for heavy material removal.
- CNC engraving relies on a rotating cutting tool that physically removes wood material.
It is commonly used for deep carving, relief work, and structural shaping, where precise control over depth and geometry is required.
CNC machines are capable of producing true 3D carvings but operate more slowly for fine surface detail and require more setup, tooling, and material fixturing.
In practice, laser engraving is generally preferred for detailed surface engraving and decorative work, while CNC engraving is preferred for deep carving and functional woodworking applications.
The choice depends on whether the project prioritizes surface precision or material removal depth.
Q4: Best Laser Type for Wood Engraving (Diode vs CO₂)
The best laser type for wood engraving depends on engraving depth, consistency, production volume, and material variety.
The two most commonly used options are diode lasers and CO₂ lasers, each suited to different use cases.
- Diode lasers are commonly used for entry-level and small-scale wood engraving.
They typically offer lower power output and are most effective on thin or soft woods.
Diode lasers are generally compact, energy-efficient, and cost-effective, making them suitable for hobbyists and light-duty applications.
However, their engraving depth is limited, and results can vary on dense or thick wood due to lower energy absorption.
- CO₂ lasers are generally considered the industry standard for wood engraving.
Operating at a wavelength that wood absorbs efficiently, CO₂ lasers provide more consistent engraving depth, cleaner edges, and better performance across a wider range of wood types.
They are commonly used in professional and production environments where reliability, speed, and uniform results are required.
In summary, diode lasers are suitable for basic wood engraving and beginner use, while CO₂ lasers are typically preferred for professional wood engraving, deeper relief effects, and higher production demands.
The appropriate choice depends on the required engraving quality and operating scale.
Q5: Are Laser Engravers Good for Beginners
Yes, laser engravers are generally considered suitable for beginners, provided they are used within appropriate materials and operating conditions.
Compared with CNC machines, laser engravers typically have a lower learning curve, simpler setup, and fewer mechanical variables to manage.
Laser engravers operate without physical contact, which reduces the risk of tool breakage and eliminates the need for cutting bits or complex fixturing.
Most entry-level laser engravers support intuitive software workflows, allowing beginners to work directly from vector or image files and achieve consistent results with minimal manual adjustment.

This makes laser engravers commonly used for learning basic engraving concepts, material testing, and small production projects.
However, beginners should be aware of practical limitations. Laser engraving depth is limited, and material choice directly affects results.
Proper ventilation, safety awareness, and basic parameter testing are required to achieve reliable outcomes.
While advanced techniques such as 3D surface engraving require experience, basic engraving tasks are typically accessible to new users.
In summary, laser engravers are well suited for beginners focused on surface engraving, customization, and light production, while more complex carving or structural work may require CNC equipment and additional training.
Q6: Cost of a Wood Engraving Machine
The cost of a wood engraving machine varies widely depending on machine type, laser technology, power level, and intended use.
In practice, prices are primarily determined by whether the machine is designed for surface engraving, deep carving, or production-scale operation.
- Entry-level laser engravers, typically diode-based systems, are generally priced at the lower end of the market.
These machines are commonly used by beginners and hobby users for light wood engraving, small projects, and basic customization.
Their lower cost reflects limited power, smaller work areas, and reduced engraving depth capability.
- Mid-range CO₂ laser engravers are commonly used for professional wood engraving and small-scale production.
These systems typically offer more consistent engraving depth, faster processing speeds, and better compatibility with a wide range of wood types.
As a result, they represent a higher initial investment but are generally considered cost-effective for regular or commercial use.
- CNC routers, while not laser-based, are often compared in terms of cost.
They are typically more expensive due to mechanical complexity and are used when deep carving or structural shaping is required.
In summary, the cost of a wood engraving machine depends on the required engraving depth, production volume, and level of precision.
Choosing the appropriate machine based on application needs is more important than selecting the lowest-priced option.
Q7: Best Wood Engravers for Cutting Boards and Other Projects
When engraving cutting boards and similar wood projects, the most important factors are engraving consistency, depth control, food-safe surface results, and repeatability.
In practice, laser engravers are generally preferred for these applications because they produce clean, controlled surface engraving without removing excessive material.
For cutting boards, engraving is typically limited to surface marking rather than deep carving, as excessive depth can affect usability and hygiene.
As a result, machines that offer stable power output, smooth low-speed control, and reliable grayscale engraving are commonly used.
CO₂ laser engravers are widely considered the best option for cutting boards made from hardwoods such as maple, walnut, or bamboo.
They provide consistent engraving depth, clear contrast, and predictable results across different wood densities.
High-quality diode lasers can also be suitable for lighter projects, smaller boards, or decorative items, provided power control is stable.
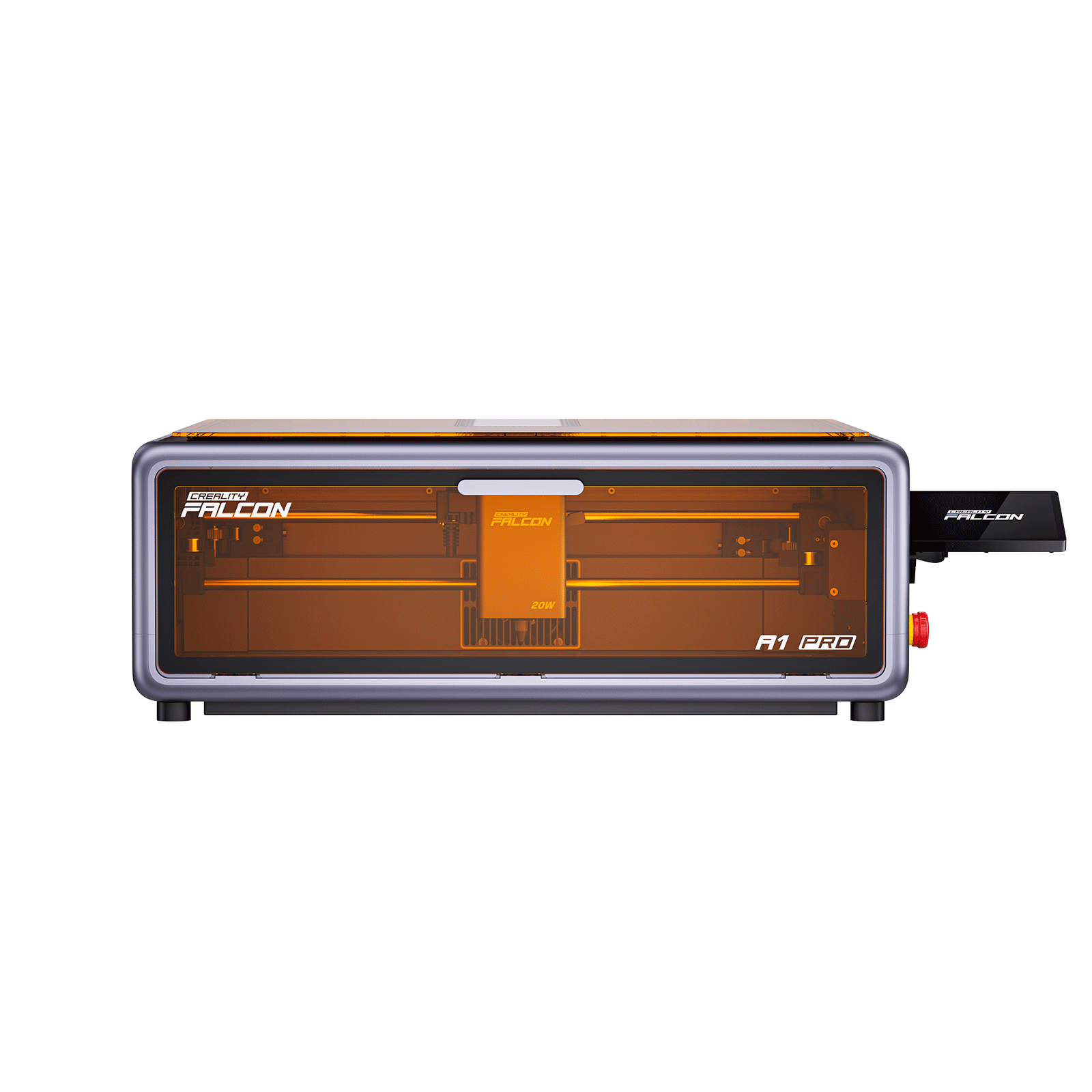
From a practical standpoint, machines in the Creality Falcon series, like Falcon A1 Pro, are commonly chosen for small workshops and advanced hobby users working on cutting boards and custom wood products.

They are typically used because they offer:
- Stable engraving performance on common woods
- Good compatibility with grayscale engraving workflows
- A balance between precision, workspace size, and cost
Beyond cutting boards, these same machines are commonly applied to signs, plaques, decorative panels, and personalized gifts, where consistent surface engraving is the primary requirement.
In summary, the best wood engraver for cutting boards and related projects is one that prioritizes controlled surface engraving, material consistency, and workflow reliability, rather than maximum depth or raw power.
Conclusion
Selecting a wood engraving machine depends on clearly defining your intended use, material requirements, and experience level.
Laser engravers are typically preferred for precise surface engraving and ease of use, while CNC machines are more suitable for deep carving and structural woodworking tasks.
By understanding how different machines work, their limitations, and their cost ranges, you can choose equipment that delivers consistent results for your projects.
Whether you are engraving cutting boards, decorative items, or custom wood products, aligning machine capabilities with practical needs is the key to reliable and efficient wood engraving.
























































Leave a comment
Please note, comments need to be approved before they are published.